Experiencing a scenario where your download speed is slower than upload can be confusing, especially when you expect download to be the dominant figure. While a slight asymmetry is often normal due to how Internet Service Providers (ISPs) provision connections, a significant disparity, or even upload speeds exceeding download speeds, usually points to an underlying problem that needs investigation. This isn't just a minor annoyance; it can severely impact your ability to stream, browse, game, and work efficiently.
⚡ Quick Verdict:
- ✅ Yes for slight differences (download slightly slower) due to ISP asymmetrical provisioning.
- ⚠️ Maybe for significant differences (download much slower) indicating a network bottleneck or interference.
- ❌ No for upload speed being faster than download speed – this is abnormal and requires immediate troubleshooting.
- 👉 Key Factor: Understanding normal ISP behavior vs. actual hardware/software issues is critical.
Why is My Download Speed Slower Than Upload? The Core Reasons
When you run a speed test and find your download speeds lagging behind your upload, there are primarily two categories of reasons: normal ISP provisioning, and abnormal network or device issues. Understanding which category you fall into is the first step to diagnosing and resolving the problem.
ISP Asymmetrical Provisioning: The "Normal" Scenario
For most residential internet connections, it's entirely normal and expected for the download speed to be significantly higher than the upload speed. This is known as asymmetrical provisioning, and it's how ISPs design their networks based on typical user behavior.
Think about how you use the internet:
- Downloading: You download web pages, stream videos, download games, and receive emails. This data flows to your device.
- Uploading: You send emails, upload photos, make video calls, and play online games (sending small data packets). This data flows from your device.
Since the vast majority of internet activity involves downloading data, ISPs allocate more bandwidth to download speeds to optimize their network for the average user. This means if you have a 100 Mbps download / 20 Mbps upload plan, your download speed is five times faster than your upload. In this scenario, if your speed test shows 90 Mbps download and 18 Mbps upload, your download is technically "slower" relative to the upload if you were expecting them to be equal, but it's performing as expected for an asymmetrical connection. The specific issue of download speed slower than upload only becomes truly problematic when the upload speed is faster than the download, or when the download speed is drastically lower than what your plan promises, even if it's still higher than the upload.
Common Causes When Upload Speed is Faster Than Download
If your speed test results show that your upload speed is actually higher than your download speed, or if your download speed is dramatically underperforming while upload remains strong, this is usually a clear sign of an issue. This is not normal ISP behavior and indicates a problem within your network, device, or connection.
Here are the most common culprits when your download speed is slower than upload in an abnormal way:
1. Wi-Fi Interference and Signal Issues
Wireless connections are susceptible to various forms of interference, which can disproportionately affect download performance.
- Distance and Obstacles: The further you are from your router, or the more walls/floors between you, the weaker the Wi-Fi signal.
- Network Congestion: Too many devices on the same Wi-Fi network can slow things down.
- Interference from Other Devices: Other Wi-Fi networks (from neighbors), Bluetooth devices, microwaves, and cordless phones can all disrupt your signal.
- Outdated Wi-Fi Standards: Older routers or device Wi-Fi adapters might not support the latest, faster standards (e.g., Wi-Fi 6/E).
2. Router or Modem Problems
Your network hardware is the gateway to the internet. If it's struggling, your speeds will suffer.
- Outdated Firmware: Router firmware updates often include performance improvements and bug fixes.
- Overheating: Routers can overheat, leading to performance degradation.
- Hardware Failure: Like any electronic device, routers and modems can simply fail or become less efficient over time.
- Poor Placement: Placing your router in a cabinet, behind a TV, or in a corner can obstruct its signal.
3. Faulty or Damaged Cables
A physical connection issue can often be the root cause.
- Ethernet Cables: Damaged, kinked, or low-quality Ethernet cables (e.g., Cat5 instead of Cat5e/Cat6 for higher speeds) can bottleneck your connection.
- Coaxial Cables (for cable internet): Loose connections, damaged insulation, or old coaxial cables can introduce signal noise and reduce speeds.
- Fiber Optic Cables: While less common to be damaged by users, kinks or severe bends in fiber lines can drastically reduce performance.
4. Device-Specific Issues
Sometimes the problem isn't the network, but the device you're testing on.
- Outdated Network Drivers: Your computer's network adapter drivers might be old or corrupted.
- Limited Hardware: An older computer with a slower processor or insufficient RAM might struggle to process high download speeds.
- Background Applications: Downloads, updates, or cloud syncing services running in the background can consume significant bandwidth.
5. VPN or Security Software Interference
While essential for privacy and security, these tools can sometimes impact speed.
- VPN Overhead: Encrypting and routing traffic through a VPN server adds overhead, which can reduce speeds, especially if the server is far away or overloaded.
- Firewalls/Antivirus: Overly aggressive security software can sometimes interfere with network traffic, slowing down transfers.
6. Server-Side Limitations
The issue might not be your connection, but the server you're connecting to.
- Website/Server Bandwidth: If the server you're downloading from is overloaded or has limited bandwidth, your download speed will be capped, regardless of your internet plan.
- Geographical Distance: Connecting to a server far away can introduce latency and reduce effective speeds.
7. Malware or Viruses
Malicious software can secretly consume your bandwidth by sending data, participating in botnets, or conducting background activities.
- Spyware/Adware: These can generate background traffic.
- Viruses/Worms: Can actively use your internet connection for various nefarious purposes, making your download speed slower than upload or just generally slow.
How to Diagnose and Fix a Slow Download Speed (Even if Upload is Faster)
When you're facing a scenario where your download speed is slower than upload, systematic troubleshooting is key. Don't jump to conclusions; follow these steps to pinpoint the problem.
Step-by-Step Troubleshooting Guide
-
Verify Your Internet Plan:
- First, confirm the download and upload speeds you're actually paying for. Check your ISP contract or log into your online account. This gives you a baseline for what to expect.
-
Test with Multiple Devices:
- Run speed tests on at least two different devices (e.g., laptop, smartphone, tablet).
- If only one device has the issue, the problem is likely with that specific device. If all devices show the same problem, the issue is likely with your network or ISP.
-
Wired vs. Wireless Test:
- Connect a computer directly to your router (or modem) using an Ethernet cable.
- Run a speed test. If speeds improve significantly compared to Wi-Fi, your Wi-Fi network is the bottleneck. If speeds remain poor, the issue is upstream (router, modem, or ISP).
Connection Type Pros Cons Wired (Ethernet) - Most stable and fastest connection - Less flexible, requires cables - Less susceptible to interference - Limited by port availability Wireless (Wi-Fi) - Flexible, allows mobility - Prone to interference and signal degradation - Easy to connect multiple devices - Often slower than wired for high speeds 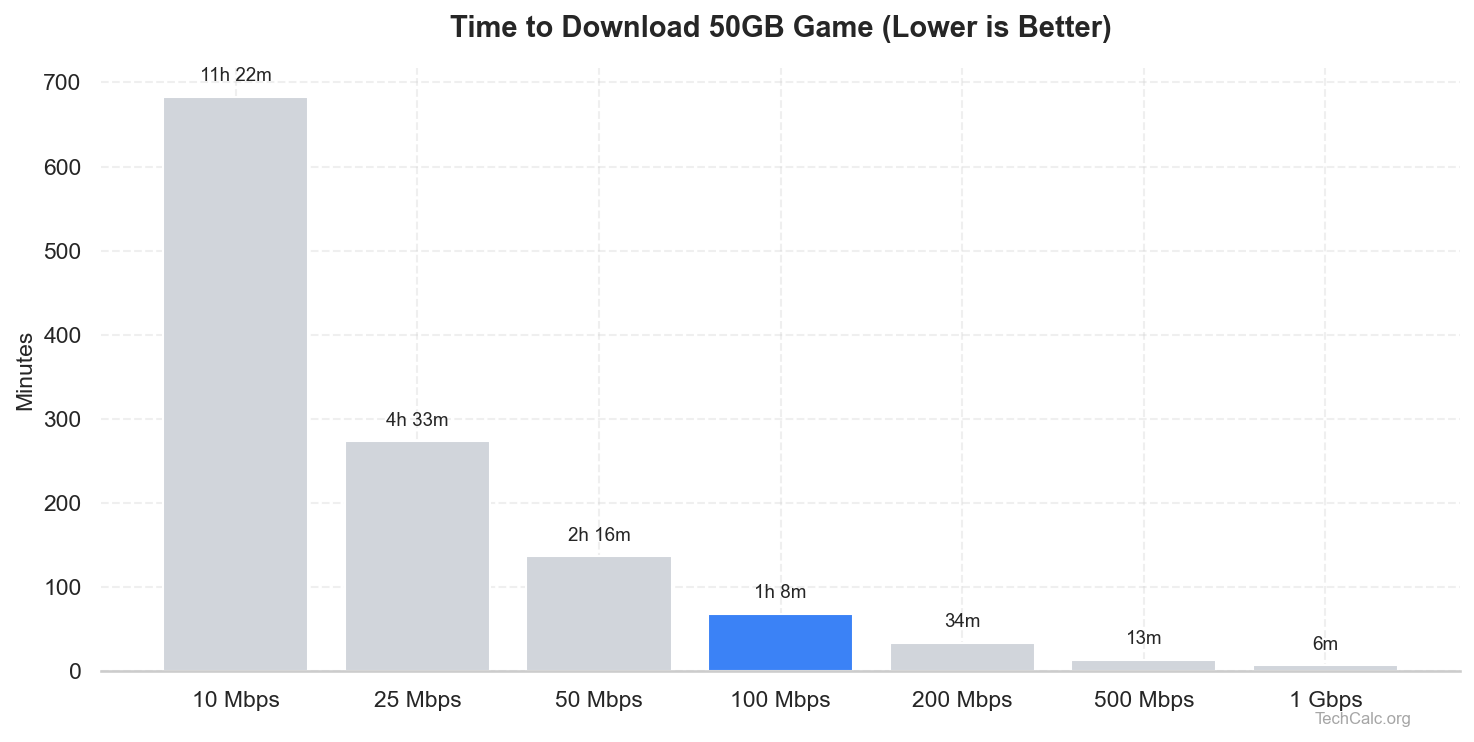
-
Bypass Your Router (Connect Directly to Modem):
- If you have a separate modem and router, try connecting your computer directly to the modem with an Ethernet cable.
- Important: Power cycle both the modem and your computer before testing.
- If speeds are good when connected to the modem, your router is the problem. If speeds are still poor, the issue lies with your ISP or the incoming line.
-
Power Cycle Your Network Hardware:
- Unplug your modem and router from power for at least 30 seconds.
- Plug the modem back in first, wait for its lights to stabilize (usually 1-2 minutes), then plug in the router.
- This simple step can often resolve temporary glitches.
-
Update Drivers and Firmware:
- Network Adapter Drivers: On your computer, ensure your network card drivers are up to date. Visit your computer manufacturer's website or the network card manufacturer's site.
- Router Firmware: Log into your router's admin interface (usually via a web browser, check your router's manual for the IP address and login details) and check for firmware updates.
-
Check for Background Activity & Malware:
- Close all unnecessary applications and browser tabs.
- Open your computer's Task Manager (Windows) or Activity Monitor (macOS) to see if any processes are consuming significant network bandwidth.
- Run a full scan with reputable antivirus/anti-malware software to rule out infections that could be hogging your bandwidth.
-
Test in Safe Mode with Networking (Windows):
- Boot your Windows PC into Safe Mode with Networking. This loads only essential drivers and services, which can help determine if third-party software is causing the issue. If speeds improve here, a software conflict is likely.
-
Contact Your Internet Service Provider (ISP):
- If you've tried all the above steps and your download speed is slower than upload or significantly below your plan, it's time to contact your ISP.
- They can run diagnostics on your line, check for outages in your area, and potentially send a technician. Be prepared to share your troubleshooting steps.
Understanding Download vs. Upload Speed
To fully grasp why your download speed is slower than upload (or should be), it's important to differentiate between these two fundamental metrics of internet performance.
- Download Speed (Downstream): This measures how quickly data travels from the internet to your device. It's crucial for activities like streaming video, loading web pages, downloading files, and online gaming (receiving game data). This is typically the higher number in consumer internet plans.
- Upload Speed (Upstream): This measures how quickly data travels from your device to the internet. It's important for activities such as sending emails with large attachments, uploading photos/videos to cloud services, making video calls (sending your video feed), and online gaming (sending your actions to the server).
As discussed, consumer internet connections are designed to prioritize download speeds because most users consume far more data than they produce. This asymmetrical design is efficient for ISPs and cost-effective for consumers. Only in specific scenarios, like running a web server, professional video streaming, or heavy cloud backups, do users typically require symmetrical (equal download and upload) speeds, which are often found in business-grade or specialized fiber plans.
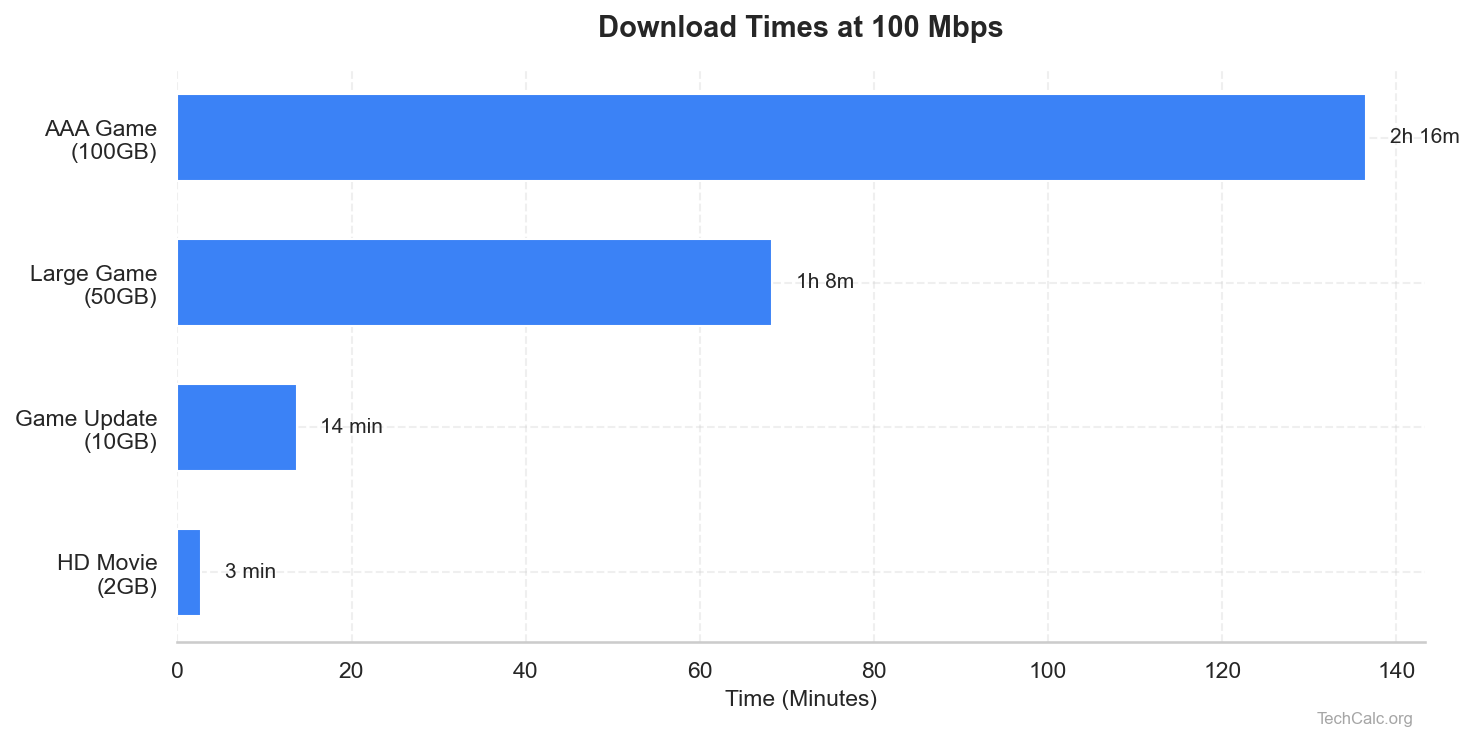
You can use our Download Time Calculator to see how different download speeds impact the time it takes to get your files. For example, a 50 Mbps connection might be fine for streaming, but if your download speed is slower than upload and you're only getting 5 Mbps download, even small files will take ages.
The Impact of Download Speed on Your Daily Activities
Even if your upload speed is healthy, a poor download speed can cripple your internet experience. Here's a quick look at how different activities are affected:
| Activity | Recommended Download Speed (Minimum) | Impact of Slow Download Speed |
|---|---|---|
| Basic Web Browsing | 1-5 Mbps | Slow page loading, images/videos buffering |
| Email & Social Media | 1-5 Mbps | Attachments take long to open, feeds update slowly |
| SD Streaming (e.g., Netflix) | 3 Mbps | Frequent buffering, blurry picture |
| HD Streaming (1080p) | 5-8 Mbps (per stream) | Constant buffering, reduced resolution, frustrating experience |
| 4K Streaming (UHD) | 25-50 Mbps (per stream) | Impossible or unwatchable, severe buffering |
| Online Gaming | 3-10 Mbps | High ping, lag, disconnections, slow game updates |
| Video Conferencing (HD) | 5-10 Mbps (per participant) | Pixelated video, audio dropouts, frozen screens |
| Large File Downloads | 25+ Mbps | Extremely long wait times, missed deadlines |
If your download speed is slower than upload to the point where it falls below these recommendations, you'll definitely notice a degraded experience. Our Download Time Calculator can help you visualize how long downloads would take at your current speed. For instance, if you're stuck with a download speed of 10 Mbps, a 5GB game update would take over an hour.
When Your Download Speed is Slower Than Upload: Real-World Scenarios and PAA Questions
Let's address some common questions and scenarios related to having a download speed that's unexpectedly low, especially when your upload is performing well.
Is it normal to have higher upload than download speed?
No, it is generally not normal for residential internet connections to have a higher upload speed than download speed. As explained earlier, ISPs provision connections asymmetrically, meaning download speed is almost always significantly higher than upload speed. If your speed test shows your upload speed consistently higher than your download speed, it indicates an underlying problem that needs to be investigated. This is a key indicator that something is wrong with your connection, device, or network configuration, and it's not simply "how your ISP set it up."
What causes upload speed to be higher than download?
When your upload speed is higher than your download, it's a strong sign of a fault. The causes are usually related to:
- Severe Download Bottleneck: Something is severely restricting your inbound data flow. This could be a damaged cable, a malfunctioning modem or router, or heavily congested Wi-Fi.
- Network Interface Card (NIC) Issues: A problem with your device's network adapter, either hardware or outdated drivers, can specifically impair download performance while upload remains functional.
- Software Interference: Overly aggressive firewalls, VPNs misconfigured, or even malware can specifically throttle download traffic.
- ISP Line Problem: While less common for it to affect download only and leave upload untouched, a specific line fault or signal issue could, in rare cases, manifest this way.
The key is that the path for upload and download data, while shared, has distinct components and potential failure points. When download is the sole sufferer, the problem is usually specific to that direction of traffic.
How do I fix my download speed if my upload speed is faster?
If your download speed is slower than upload to the point where upload is faster, you need to systematically troubleshoot. Here's a condensed action plan:
- Isolate the Device: Test on another device. If the problem persists, it's network-wide. If not, troubleshoot the original device (drivers, malware, background apps).
- Bypass Wi-Fi: Connect via Ethernet. If speeds improve, address Wi-Fi interference (move router, change channels, update router).
- Bypass Router: Connect directly to the modem. If speeds improve, your router is faulty or misconfigured (reset, update firmware, consider replacement).
- Check Cables: Inspect all Ethernet and coaxial/fiber cables for damage. Replace any suspicious ones.
- Software Check: Disable VPNs, firewalls, and run a malware scan.
- Contact ISP: If all else fails, the problem is likely with their equipment or the line coming into your home.
This methodical approach will help you narrow down the exact cause when your upload speed is unexpectedly superior to your download speed.
Can a bad router cause upload to be faster than download?
Yes, a bad or malfunctioning router can absolutely cause your download speed to be slower than upload, or even for your upload speed to be faster than your download speed. Here's why:
- Internal Hardware Failure: Components within the router responsible for processing inbound (download) traffic might be failing, while those handling outbound (upload) traffic are still functional.
- Firmware Bugs: Corrupted or outdated router firmware can introduce bugs that disproportionately affect download performance.
- Overheating: An overheating router can lead to inconsistent performance, often manifesting as speed drops in one direction.
- Congestion/Packet Loss: A struggling router might drop more download packets than upload packets, leading to retransmissions and perceived slower download speeds.
- QoS (Quality of Service) Misconfiguration: If QoS settings are incorrectly configured, they could inadvertently prioritize upload traffic or throttle download traffic.
Testing by connecting directly to your modem (bypassing the router) is the best way to confirm if your router is the culprit. If your speeds normalize when the router is out of the picture, then it's time to troubleshoot, reset, or replace your router.
Conclusion
Finding your download speed slower than upload is rarely a sign of a healthy internet connection, unless the "slower" part is merely a slight difference in an asymmetrically provisioned plan. If your upload speed is actually faster than your download speed, or if your download speed is drastically underperforming, it's a clear indicator of a problem.
From Wi-Fi interference and faulty cables to outdated router firmware or even malware, numerous factors can contribute to this frustrating issue. By systematically troubleshooting your network—starting with device-specific checks, moving to wired connections, and then isolating your router and modem—you can effectively pinpoint the source of the slowdown. Remember to leverage tools like our Download Time Calculator to understand the practical implications of your speeds. Don't settle for a sub-optimal connection; a little investigation can restore your internet performance to its full potential in 2025.