Is 100 Mbps download speed slow in 2026? The short answer is no, 100 Mbps is generally not considered slow for the average household in 2026. For a single user or a small family (2-3 people), 100 Mbps is perfectly adequate for streaming 4K video, online gaming, and multiple video calls simultaneously. However, here's the catch that internet service providers (ISPs) often overlook: raw download speed isn't the only metric that matters. Latency, network congestion, and the number of active users in your home can quickly make even a seemingly fast 100 Mbps connection feel sluggish. If you have 4+ people constantly streaming, gaming, and downloading large files, you might start experiencing slowdowns.
⚡ Quick Verdict:
- ✅ Yes for 1-3 people streaming 4K, gaming, and working from home
- ⚠️ Maybe for 4-5 people with moderate to heavy simultaneous use
- ❌ No for 6+ people or very heavy, constant simultaneous high-bandwidth activities
- 👉 Key Factor: Latency and household size often matter more than raw speed
Understanding Download Speed: Mbps vs. MBps
Before we dive into what makes a good connection, let's clarify a crucial distinction that often confuses people: the difference between Mbps and MBps.
- Mbps (Megabits per second): This is how ISPs advertise internet speeds. A megabit is a unit of data measurement.
- MBps (Megabytes per second): This is what you usually see when downloading files in your browser or a game client. A megabyte is also a unit of data, but much larger than a megabit.
The critical conversion is: 1 MBps = 8 Mbps.
So, if your ISP promises 100 Mbps, your actual download speed, as seen in your browser, will be around 12.5 MBps (100 / 8 = 12.5). This difference is why a "100 Mbps" connection might feel slower than expected if you're thinking in terms of megabytes. Our Download Time Calculator uses Mbps for input but helps you visualize the time in minutes and seconds, taking this conversion into account.
What is a Good Download Speed in 2026?
"Good" is subjective and depends entirely on your household's internet usage. However, based on typical activities, here's a general guideline for what's considered a good download speed:
- Basic Use (Email, Browsing, Light Streaming): 25-50 Mbps
- Moderate Use (HD Streaming, Online Gaming, Video Calls for 1-2 users): 50-100 Mbps
- Heavy Use (4K Streaming, Multiple Gamers, Large Downloads, Smart Home Devices for 3-5 users): 100-300 Mbps
- Very Heavy Use (Multiple 4K Streams, Professional Gaming, Large File Transfers, Multiple Users/Devices): 300-1000+ Mbps (Gigabit)
Keep in mind these are minimum recommendations. Having a buffer is always better, especially as more devices connect to your network.
Download Speed Requirements for Common Activities
To truly understand if your internet speed is sufficient, consider what you and your household do online. Here's a breakdown of typical download speed requirements for popular activities:
| Activity | Minimum Recommended Download Speed (Mbps) | Optimal Download Speed (Mbps) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Definition (SD) Stream | 3 | 5 | Single stream |
| High Definition (HD) Stream | 5-8 | 10-15 | Single stream (1080p) |
| Ultra HD (4K) Stream | 15-25 | 25-50 | Single stream, Netflix recommends 25 Mbps |
| Online Gaming (Casual) | 10-20 | 25-50 | Speed less critical than latency/ping |
| Online Gaming (Competitive) | 25-50 | 50-100+ | Prioritize low latency, stable connection |
| Video Conferencing (HD) | 5-10 | 10-20 | For smooth, clear calls (Zoom, Teams) |
| Web Browsing/Email | 1-5 | 5-10 | Almost any broadband speed is fine |
| Large File Downloads | 50+ | 100-500+ | Depends on file size and how quickly you need it |
| Smart Home Devices | 1-2 (per device) | 5-10 | Security cameras, smart speakers, etc. add to total bandwidth needs |
As you can see, a single 4K stream needs about 25 Mbps. If two people are streaming 4K, that's 50 Mbps. Add a gamer needing 20 Mbps and someone on a video call at 10 Mbps, and you're already at 80 Mbps. This quickly eats into your 100 Mbps allowance, highlighting why household size and simultaneous usage are key.
Is 100 Mbps Download Speed Slow in 2026? (PAA Deep Dive)
While 100 Mbps is generally not slow, its perceived "slowness" hinges on several factors:
- Number of Users and Devices: The more people and devices actively using the internet in your home, the more bandwidth is consumed. A family of five with multiple devices streaming, gaming, and working simultaneously will find 100 Mbps far less adequate than a single individual.
- Activity Type: As detailed above, 4K streaming and large file downloads are bandwidth hogs. If your family regularly engages in these activities concurrently, 100 Mbps might feel restrictive.
- Latency (Ping): For online gaming, latency (or ping) is often more critical than raw download speed. Latency is the time it takes for a data packet to travel from your device to the server and back. High latency leads to "lag," even if your download speed is excellent. 100 Mbps doesn't guarantee low latency.
- Wi-Fi vs. Wired Connection: Wi-Fi introduces overhead and potential interference, which can reduce your effective speed. A wired Ethernet connection will almost always provide a more stable and faster experience, especially for gaming and critical work.
- Network Hardware: Your router's age and quality play a significant role. An old, outdated router might not be able to handle 100 Mbps efficiently, acting as a bottleneck.
- ISP Throttling and Congestion: During peak hours, your ISP might experience network congestion, leading to slower speeds for everyone in your area. Some ISPs also practice traffic shaping or throttling, which can impact specific types of data.
So, while 100 Mbps is a solid baseline, it's not a magic bullet. If you're experiencing slowdowns, it might not be the raw speed itself, but one of these other factors.
How to Use a Download Speed Calculator
Our Download Time Calculator at TechCalc is designed to help you understand how long various downloads will take at your specific internet speed. This is incredibly useful for planning large downloads, understanding if your current speed is sufficient for your needs, or even comparing potential ISP plans.
Here's how it works:
- Enter Your Download Speed: Input your internet speed in Mbps. You can get this from an internet speed test.
- Enter File Size: Specify the size of the file you want to download (e.g., 500 MB, 10 GB).
- Calculate: The tool instantly estimates the time it will take to download that file.
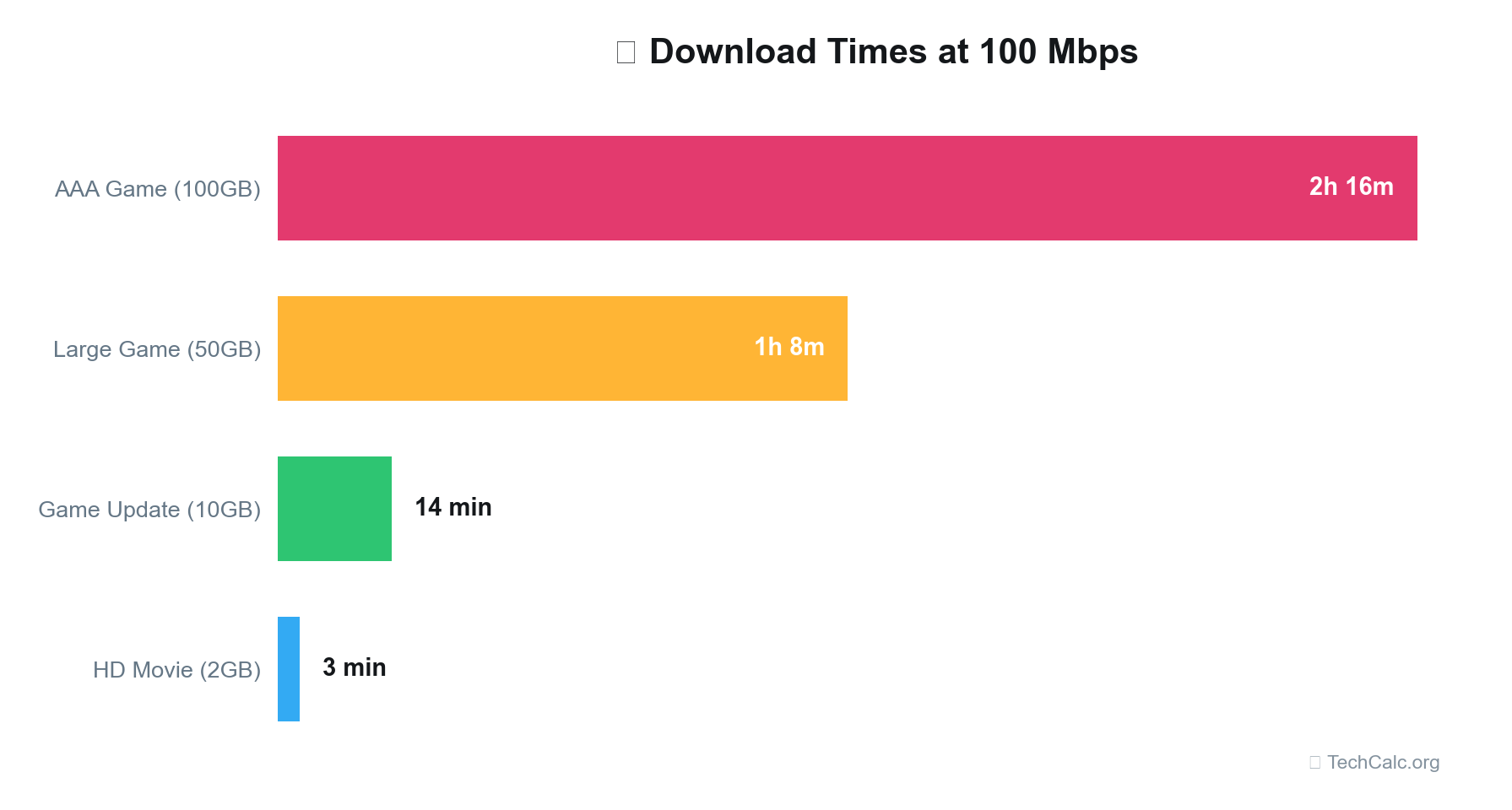
This simple tool demystifies the relationship between file size, speed, and time. For instance, if you're wondering how long it would take to download a 20 GB game update on a 100 Mbps connection, our calculator can give you an immediate answer (roughly 26 minutes and 40 seconds).
Typical Download Times for Various File Sizes
Let's put some numbers to the test using a typical 100 Mbps download speed and other common tiers. This table illustrates how quickly various file sizes can be downloaded, assuming optimal conditions and no significant overhead.
| File Size | 50 Mbps (approx. 6.25 MBps) | 100 Mbps (approx. 12.5 MBps) | 250 Mbps (approx. 31.25 MBps) | 500 Mbps (approx. 62.5 MBps) | 1000 Mbps (approx. 125 MBps) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 MB | 16 seconds | 8 seconds | 3 seconds | 2 seconds | 1 second |
| 500 MB | 1 minute 20 seconds | 40 seconds | 16 seconds | 8 seconds | 4 seconds |
| 1 GB (1000 MB) | 2 minutes 40 seconds | 1 minute 20 seconds | 32 seconds | 16 seconds | 8 seconds |
| 5 GB | 13 minutes 20 seconds | 6 minutes 40 seconds | 2 minutes 40 seconds | 1 minute 20 seconds | 40 seconds |
| 20 GB | 53 minutes 20 seconds | 26 minutes 40 seconds | 10 minutes 40 seconds | 5 minutes 20 seconds | 2 minutes 40 seconds |
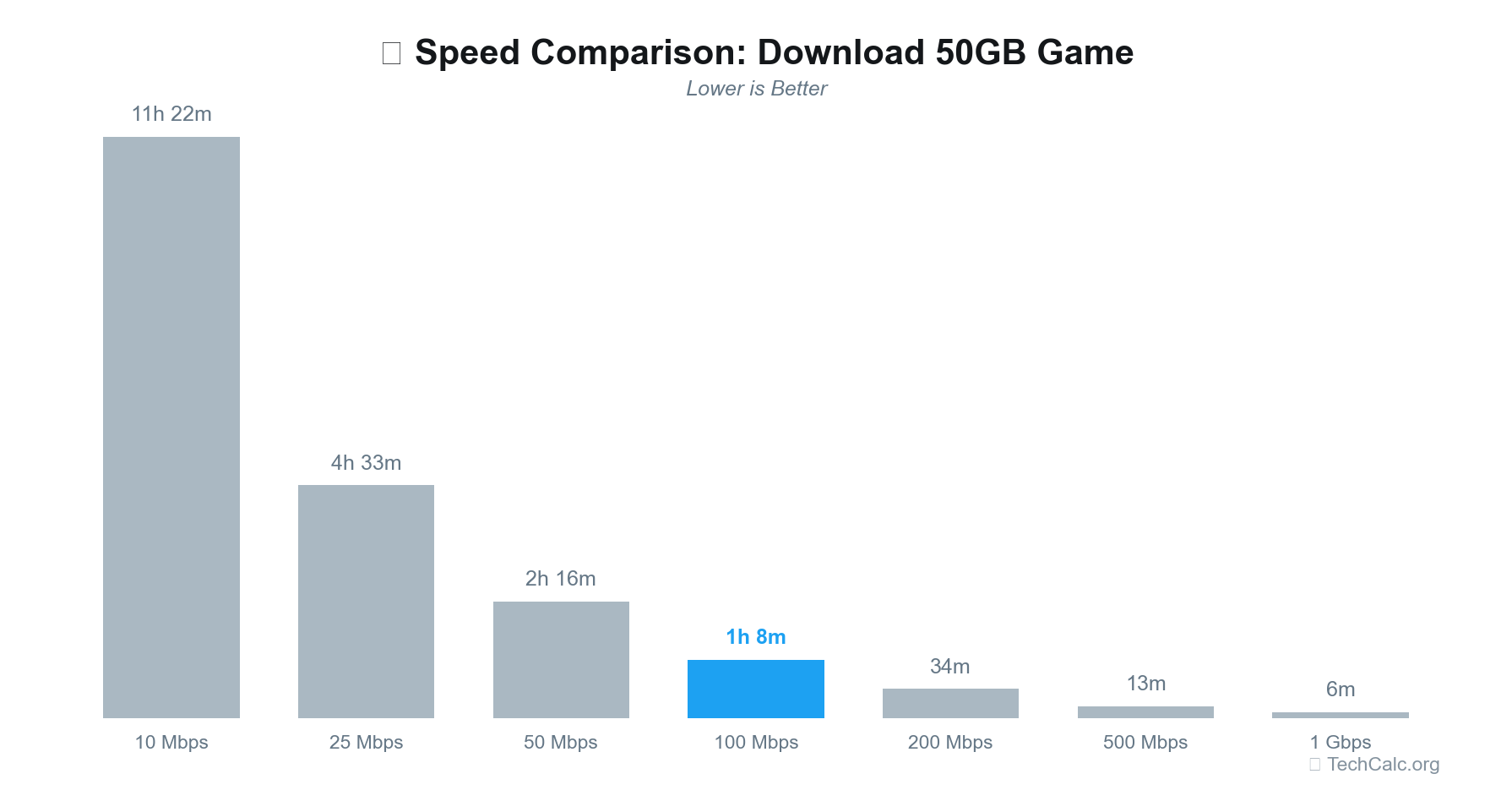
| 50 GB | 2 hours 13 minutes | 1 hour 6 minutes | 26 minutes 40 seconds | 13 minutes 20 seconds | 6 minutes 40 seconds |
This table clearly demonstrates the significant time savings as your download speed increases, especially for larger files like game updates or 4K movies. For example, downloading a 50GB game on a 50 Mbps connection takes over two hours, while on a 1000 Mbps connection, it's done in under 7 minutes.
Factors Affecting Your Real-World Download Speed
The advertised speed from your ISP is often the theoretical maximum. Your actual, real-world experience can be influenced by many variables:
- Wi-Fi Signal Strength and Interference: Walls, distance, and other wireless devices can degrade your Wi-Fi signal, slowing down your connection.
- Router Quality and Placement: An old or poorly placed router can be a bottleneck. Central placement and newer Wi-Fi 6/6E routers can significantly improve performance.
- Network Congestion: If many people in your neighborhood are online simultaneously, especially during peak hours, your speed might drop.
- Server Speed and Location: The speed at which the server you're downloading from can send data (its upload speed) and its geographical distance from you can impact your download speed.
- Cable/Infrastructure Issues: Damaged cables or outdated infrastructure in your home or neighborhood can limit your speeds.
- Number of Connected Devices: Every device connected to your network, even if idle, consumes some bandwidth and can contribute to slowdowns.
- Background Processes: Updates for your operating system, cloud backups, or other apps running in the background can consume bandwidth.
Speed Comparison: What Do Different Tiers Offer?
Let's look at how different common download speed tiers stack up against each other and what they mean for your daily online activities. This comparison highlights the jump in capability as you move up the speed ladder.
| Speed Tier | Primary Use Case | Ideal For | Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| 25-50 Mbps | Basic browsing, single HD stream, light gaming | 1-2 users, email, social media, occasional streaming | Can struggle with multiple HD streams or concurrent large downloads. |
| 50-100 Mbps | Moderate household use, 4K streaming, online gaming | 2-3 users, multiple HD/single 4K stream, online gaming, remote work/school | Excellent all-rounder, but can be stretched with 4+ heavy users. |
| 100-300 Mbps | Heavy household use, multiple 4K streams, serious gaming | 3-5 users, multiple 4K streams, competitive gaming, significant smart home usage | Great for most demanding households, provides ample buffer. |
| 300-500 Mbps | Very heavy use, large file transfers, future-proofing | 5+ users, professional streaming/content creation, very fast large downloads | Offers substantial headroom, minimizes buffering even with extreme use. |
| 500-1000+ Mbps (Gigabit) | Ultimate performance, enterprise-level home use | Power users, large families, home offices, future-proof for years to come | Virtually eliminates bandwidth as a concern for residential use. Still subject to latency. |
As you can see, 100 Mbps is a strong contender in the middle tier, offering a very good balance of performance and cost for many households.
Testing Your Download Speed
To know your actual download speed, you need to test it. There are many free online speed test tools available (e.g., Ookla Speedtest, Google Fiber Speed Test). For the most accurate results:
- Connect via Ethernet: If possible, plug your computer directly into your router with an Ethernet cable. This eliminates Wi-Fi variables.
- Close Other Applications: Ensure no other apps or devices are consuming bandwidth during the test.
- Test Multiple Times: Run the test a few times over different periods of the day to get an average.
- Test at Different Locations: If using Wi-Fi, test near your router and in areas where you typically use your devices to gauge signal strength.
Comparing these results to your advertised ISP speed will show you if you're getting what you pay for. If your actual speed is consistently much lower, it might be time to troubleshoot or contact your ISP.
Optimizing Your Internet Speed
If your 100 Mbps connection (or any speed) isn't living up to expectations, consider these optimization tips:
- Upgrade Your Router: If your router is more than 3-4 years old, or doesn't support Wi-Fi 5 (802.11ac) or Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax), an upgrade can significantly improve performance.
- Use Ethernet for Critical Devices: Connect gaming consoles, streaming boxes, and primary work computers directly to the router.
- Optimize Router Placement: Place your router in a central, open location, away from obstructions and other electronics that can cause interference.
- Restart Your Router/Modem Regularly: A simple reboot can often resolve minor performance issues.
- Check for Background Apps: Ensure no unnecessary programs are hogging bandwidth in the background.
- Consider a Mesh Wi-Fi System: For larger homes, mesh systems provide better Wi-Fi coverage than a single router.
- Review Your ISP Plan: If you consistently exceed your bandwidth needs, it might be time to upgrade your plan. Use a download speed calculator like ours to estimate future needs.
- Update Device Drivers: Ensure your network adapters on your computers are running the latest drivers.
Conclusion: Making the Most of Your Download Speed
In 2026, 100 Mbps is a robust download speed that comfortably handles the needs of most small to medium-sized households. It allows for high-quality streaming, responsive online gaming, and efficient remote work or learning. However, the true measure of your internet experience isn't just the number on your bill; it's how effectively that speed translates into seamless online activity for everyone in your home. Factors like latency, the number of simultaneous users, and the quality of your home network hardware play equally crucial roles.
Understanding the difference between Mbps and MBps, knowing your household's specific bandwidth demands, and utilizing tools like our Download Time Calculator can empower you to make informed decisions about your internet plan. Don't just pay for speed; pay for the right experience. Use our download speed calculator to see how your current or potential internet speed stacks up against your downloading needs, and ensure you're getting the most out of your connection.